Curate, connect, and discover
Space Science - Blog Posts
Fun fact about lore?
During the start of the intergalactic era, fossil fuels became dangerously scarce and the spaceships that were being built at the time were some crazy gas guzzlers, so there was a drastic crash in intergalactic travel for a few years as new technology was developed
Now, biofuel and liquid hydrogen (hydrogen fuel cells is an experimental fuel being currently worked on) are the most commonly used fuels. Fossil fuels still exist, but those that use them are considered old timey and classic, which a few love but a lot hate.
Also, liquid hydrogen systems require a nuclear core to power. The liquid hydrogen is injected into the core to create a chemical reaction which will boost the ship forward. Ships using these systems are either bi-system ships (paired with electricity, typically) or large scale cargo ships
Our Galaxy is Caught Up in a Giant Cosmic Cobweb! 🕸️

If we could zoom waaaay out, we would see that galaxies and galaxy clusters make up large, fuzzy threads, like the strands of a giant cobweb. But we'll work our way out to that. First let's start at home and look at our planet's different cosmic communities.
Our home star system
Earth is one of eight planets — Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune — that orbit the Sun. But our solar system is more than just planets; it also has a lot of smaller objects.
An asteroid belt circles the Sun between Mars and Jupiter. Beyond Neptune is a doughnut-shaped region of icy objects called the Kuiper Belt. This is where dwarf planets like Pluto and Makemake are found and is likely the source of short-period comets (like Haley’s comet), which orbit the Sun in less than 200 years.
Scientists think that even farther out lies the Oort Cloud, also a likely source of comets. This most distant region of our solar system is a giant spherical shell storing additional icy space debris the size of mountains, or larger! The outer edge of the Oort Cloud extends to about 1.5 light-years from the Sun — that’s the distance light travels in a year and a half (over 9 trillion miles).

Sometimes asteroids or comets get ejected from these regions and end up sharing an orbit with planets like Jupiter or even crossing Earth’s orbit. There are even interstellar objects that have entered the inner solar system from even farther than the Oort Cloud, perhaps coming all the way from another star!
Our home galaxy
Let's zoom out to look at the whole Milky Way galaxy, which contains more than 100 billion stars. Many are found in the galaxy’s disk — the pancake-shaped part of a spiral galaxy where the spiral arms lie. The brightest and most massive stars are found in the spiral arms, close to their birth places. Dimmer, less massive stars can be found sprinkled throughout the disk. Also found throughout the spiral arms are dense clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. The Sun lies in a small spiral arm called the Orion Spur.

The Milky Way’s disk is embedded in a spherical “halo” about 120,000 light-years across. The halo is dotted with globular clusters of old stars and filled with dark matter. Dark matter doesn’t emit enough light for us to directly detect it, but we know it’s there because without its mass our galaxy doesn’t have enough gravity to hold together!
Our galaxy also has several orbiting companion galaxies ranging from about 25,000 to 1.4 million light-years away. The best known of these are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, which are visible to the unaided eye from Earth’s Southern Hemisphere.
Our galactic neighborhood

The Milky Way and Andromeda, our nearest neighboring spiral galaxy, are just two members of a small group of galaxies called the Local Group. They and the other members of the group, 50 to 80 smaller galaxies, spread across about 10 million light-years.
The Local Group lies at the outskirts of an even larger structure. It is just one of at least 100 groups and clusters of galaxies that make up the Virgo Supercluster. This cluster of clusters spans about 110 million light-years!

Galaxies aren’t the only thing found in a galaxy cluster, though. We also find hot gas, as shown above in the bright X-ray light (in pink) that surrounds the galaxies (in optical light) of cluster Abell 1413, which is a picturesque member of a different supercluster. Plus, there is dark matter throughout the cluster that is only detectable through its gravitational interactions with other objects.
The Cosmic Web
The Virgo Supercluster is just one of many, many other groups of galaxies. But the universe’s structure is more than just galaxies, clusters, and the stuff contained within them.

For more than two decades, astronomers have been mapping out the locations of galaxies, revealing a filamentary, web-like structure. This large-scale backbone of the cosmos consists of dark matter laced with gas. Galaxies and clusters form along this structure, and there are large voids in between.
The scientific visualizations of this “cosmic web” look a little like a spider web, but that would be one colossal spider! <shudder>

And there you have the different communities that define Earth’s place in the universe. Our tiny planet is a small speck on a crumb of that giant cosmic web!
Want to learn even more about the structures in the universe? Check out our Cosmic Distance Scale!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space.
Why are bacteria resistant polymers being experimented, specifically in microgravity?
How are decisions made about what experiments are sent into space? Are there certain kinds of experiments that NASA wants to conduct every time cargo is launched to the ISS, or are there occasionally experiments that are duplicated for more observation and data collection?
How do you deal with/account for low/no gravity in space (ex. stuff floating around), if it's not a factor of the experiment? (I hope that makes sense? Words are hard)
I am interested in learning how to grow plants in space. How can I be involved in this as a college student, or independently?
When sending experiments to space, what is the most unexpected thing you have to think about? Like you're probably have to consider things like radiation damage, but what is something that isn't an immediately obvious issue that you have to account for?
What inspired you to attempt a SPOCS project?
What's a SPOC? Isn't that a star trek character?
May the Four Forces Be With You!
May the force be with you? Much to learn you still have, padawan. In our universe it would be more appropriate to say, “May the four forces be with you.”
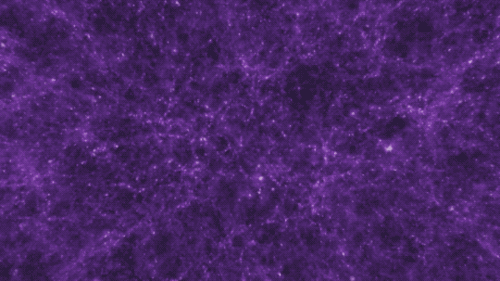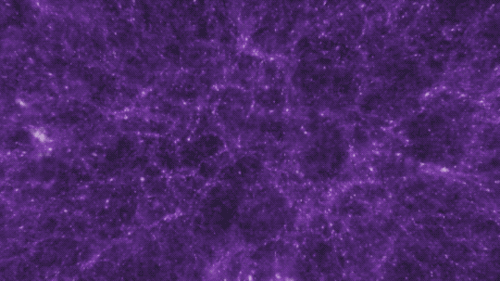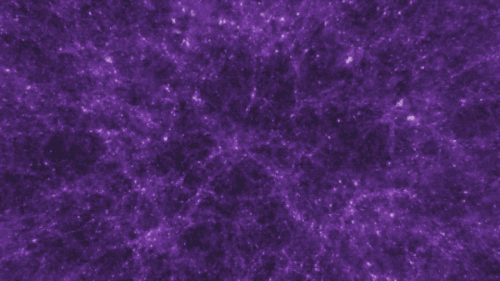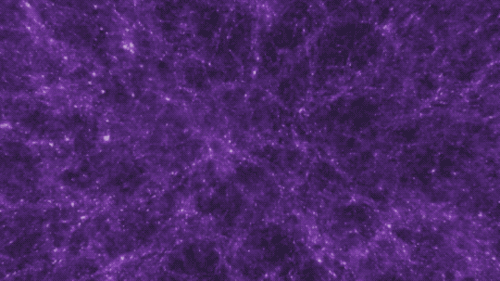
There are four fundamental forces that bind our universe and its building blocks together. Two of them are easy to spot — gravity keeps your feet on the ground while electromagnetism keeps your devices running. The other two are a little harder to see directly in everyday life, but without them, our universe would look a lot different!
Let’s explore these forces in a little more detail.
Gravity: Bringing the universe together

If you jump up, gravity brings you back down to Earth. It also keeps the solar system together … and our galaxy, and our local group of galaxies and our supercluster of galaxies.
Gravity pulls everything together. Everything, from the bright centers of the universe to the planets farthest from them. In fact, you (yes, you!) even exert a gravitational force on a galaxy far, far away. A tiny gravitational force, but a force nonetheless.

Credit: NASA and the Advanced Visualization Laboratory at the National Center for Supercomputing and B. O'Shea, M. Norman
Despite its well-known reputation, gravity is actually the weakest of the four forces. Its strength increases with the mass of the two objects involved. And its range is infinite, but the strength drops off as the square of the distance. If you and a friend measured your gravitational tug on each other and then doubled the distance between you, your new gravitational attraction would just be a quarter of what it was. So, you have to be really close together, or really big, or both, to exert a lot of gravity.
Even so, because its range is infinite, gravity is responsible for the formation of the largest structures in our universe! Planetary systems, galaxies and clusters of galaxies all formed because gravity brought them together.
Gravity truly surrounds us and binds us together.
Electromagnetism: Lighting the way
You know that shock you get on a dry day after shuffling across the carpet? The electricity that powers your television? The light that illuminates your room on a dark night? Those are all the work of electromagnetism. As the name implies, electromagnetism is the force that includes both electricity and magnetism.
Electromagnetism keeps electrons orbiting the nucleus at the center of atoms and allows chemical compounds to form (you know, the stuff that makes up us and everything around us). Electromagnetic waves are also known as light. Once started, an electromagnetic wave will travel at the speed of light until it interacts with something (like your eye) — so it will be there to light up the dark places.

Like gravity, electromagnetism works at infinite distances. And, also like gravity, the electromagnetic force between two objects falls as the square of their distance. However, unlike gravity, electromagnetism doesn't just attract. Whether it attracts or repels depends on the electric charge of the objects involved. Two negative charges or two positive charges repel each other; one of each, and they attract each other. Plus. Minus. A balance.
This is what happens with common household magnets. If you hold them with the same “poles” together, they resist each other. On the other hand, if you hold a magnet with opposite poles together — snap! — they’ll attract each other.
Electromagnetism might just explain the relationship between a certain scruffy-looking nerf-herder and a princess.
Strong Force: Building the building blocks

Credit: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
The strong force is where things get really small. So small, that you can’t see it at work directly. But don’t let your eyes deceive you. Despite acting only on short distances, the strong force holds together the building blocks of the atoms, which are, in turn, the building blocks of everything we see around us.
Like gravity, the strong force always attracts, but that’s really where their similarities end. As the name implies, the force is strong with the strong force. It is the strongest of the four forces. It brings together protons and neutrons to form the nucleus of atoms — it has to be stronger than electromagnetism to do it, since all those protons are positively charged. But not only that, the strong force holds together the quarks — even tinier particles — to form those very protons and neutrons.
However, the strong force only works on very, very, very small distances. How small? About the scale of a medium-sized atom’s nucleus. For those of you who like the numbers, that’s about 10-15 meters, or 0.000000000000001 meters. That’s about a hundred billion times smaller than the width of a human hair! Whew.
Its tiny scale is why you don’t directly see the strong force in your day-to-day life. Judge a force by its physical size, do you?
Weak Force: Keeping us in sunshine

If you thought it was hard to see the strong force, the weak force works on even smaller scales — 1,000 times smaller. But it, too, is extremely important for life as we know it. In fact, the weak force plays a key role in keeping our Sun shining.
But what does the weak force do? Well … that requires getting a little into the weeds of particle physics. Here goes nothing! We mentioned quarks earlier — these are tiny particles that, among other things, make up protons and neutrons. There are six types of quarks, but the two that make up protons and neutrons are called up and down quarks. The weak force changes one quark type into another. This causes neutrons to decay into protons (or the other way around) while releasing electrons and ghostly particles called neutrinos.
So for example, the weak force can turn a down quark in a neutron into an up quark, which will turn that neutron into a proton. If that neutron is in an atom’s nucleus, the electric charge of the nucleus changes. That tiny change turns the atom into a different element! Such reactions are happening all the time in our Sun, giving it the energy to shine.
The weak force might just help to keep you in the (sun)light.

All four of these forces run strong in the universe. They flow between all things and keep our universe in balance. Without them, we’d be doomed. But these forces will be with you. Always.
You can learn more about gravity from NASA’s Space Place and follow NASAUniverse on Twitter or Facebook to learn about some of the cool cosmic objects we study with light.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Cosmic Piece of Pi!
Did you know that pi is involved nearly anywhere you look? We’re not talking about your favorite pastry! Pi (also written as the Greek letter 𝞹, or the number 3.14159...) is an irrational number, which means it can’t be written as a simple fraction like ½. It is the ratio of a circle’s circumference (the distance around its edge) to its diameter (the distance across it) and will always be the same number, regardless of the circle’s size. Here are some places you can find pi in the universe around us!

Our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, TESS, watches slices of the sky in its hunt for worlds outside our solar system — how many exoplanets are in its night-sky pie? Last July, TESS scientists created a mosaic of 208 images of the southern sky. At that time, it contained 29 confirmed and 1,000 possible exoplanets, and we’re still studying the data to find more. Since this awe-inspiring image is of the southern hemisphere (or half of a 3D circle), there will always be pi! Every slice contains something delicious for scientists to study.

Pi recently played a crucial role in new discoveries about Alpha Draconis, a well-studied pair of stars. After discovering these stars regularly eclipse each other, pi helped scientists learn more about them. Scientists detected the eclipses while monitoring the brightness of Alpha Draconis for periodic dips that could’ve been caused by planets passing between the star and us. Instead of a planet, though, researchers found that its smaller partner in crime was passing in between us and the larger star for about six hours at a time! 💫

Pi comes in handy as we learn more about these two stars. Knowing the percentage of the decrease in Alpha Draconis’ light and the formula for the area of a circle (A=𝞹r2 — or area equals pi times the square of the circle's radius), scientists can predict the sizes of both stars. Because stars typically orbit in an elliptical (or oval) shape, pi also helps scientists use the detection of these eclipses to figure out the orbits of the two stars!
So far we’ve seen pi in many places! But it's also interesting to look at where pi can't be found! We mentioned earlier that many orbit calculations involve pi … but not every one does! Pi does not factor into calculations of hyperbolic orbits — orbits that aren't complete, or don't return to where they started — the same way that it does with elliptical orbits! This is most commonly seen with comets. While many comets orbit normally in our solar system, some oddballs just pass through, like the interstellar ‘Oumuamua that zipped passed us in 2017. ☄️

Perhaps the most popular place you may find pi is in the shape of a typical pie! While NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope studies gamma-rays, and not blueberries, we think this cool Fermi pie is worth sharing for Pi Day!
Find more ways scientists look up at the night sky and use pi here. And now, don’t be irrational, and go have some pi(e)! 🥧
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Weird Magnetic Behavior in Space
In between the planets, stars and other bits of rock and dust, space seems pretty much empty. But the super-spread out matter that is there follows a different set of rules than what we know here on Earth.
For the most part, what we think of as empty space is filled with plasma. Plasma is ionized gas, where electrons have split off from positive ions, creating a sea of charged particles. In most of space, this plasma is so thin and spread out that space is still about a thousand times emptier than the vacuums we can create on Earth. Even still, plasma is often the only thing out there in vast swaths of space — and its unique characteristics mean that it interacts with electric and magnetic fields in complicated ways that we are just beginning to understand.

Five years ago, we launched a quartet of satellites to study one of the most important yet most elusive behaviors of that material in space — a kind of magnetic explosion that had never before been adequately studied up close, called magnetic reconnection. Here are five of the ways the Magnetospheric Multiscale mission (MMS) has helped us study this intriguing magnetic phenomenon.
1. Seeing magnetic explosions up close
Magnetic reconnection is the explosive snapping and forging of magnetic fields, a process that can only happen in plasmas — and it's at the heart of space weather storms that manifest around Earth.
When the Sun launches clouds of solar material — which is also made of plasma — toward Earth, the magnetic field embedded within the material collides with Earth's huge global magnetic field. This sets off magnetic reconnection that injects energy into near-Earth space, triggering a host of effects — induced electric currents that can harm power grids, to changes in the upper atmosphere that can affect satellites, to rains of particles into the atmosphere that can cause the glow of the aurora.

Though scientists had theorized about magnetic reconnection for decades, we'd never had a chance to study it on the small scales at which it occurs. Determining how magnetic reconnection works was one of the key jobs MMS was tasked with — and the mission quickly delivered. Using instruments that measured 100 times faster than previous missions, the MMS observations quickly determined which of several 50-year-old theories about magnetic reconnection were correct. It also showed how the physics of electrons dominates the process — a subject of debate before the launch.
2. Finding explosions in surprising new places
In the five years after launch, MMS made over a thousand trips around Earth, passing through countless magnetic reconnection events. It saw magnetic reconnection where scientists first expected it: at the nose of Earth's magnetic field, and far behind Earth, away from the Sun. But it also found this process in some unexpected places — including a region thought to be too tumultuous for magnetic reconnection to happen.
As solar material speeds away from the Sun in a flow called the solar wind, it piles up as it encounters Earth's magnetic field, creating a turbulent region called the magnetosheath. Scientists had only seen magnetic reconnection happening in relatively calm regions of space, and they weren't sure if this process could even happen in such a chaotic place. But MMS' precise measurements revealed that magnetic reconnection happens even in the magnetosheath.

MMS also spotted magnetic reconnection happening in giant magnetic tubes, leftover from earlier magnetic explosions, and in plasma vortices shaped like ocean waves — based on the mission's observations, it seems magnetic reconnection is virtually ubiquitous in any place where opposing magnetic fields in a plasma meet.
3. How energy is transferred
Magnetic reconnection is one of the major ways that energy is transferred in plasma throughout the universe — and the MMS mission discovered that tiny electrons hold the key to this process.
Electrons in a strong magnetic field usually exhibit a simple behavior: They spin tight spirals along the magnetic field. In a weaker field region, where the direction of the magnetic field reverses, the electrons go freestyle — bouncing and wagging back and forth in a type of movement called Speiser motion.

Flying just 4.5 miles apart, the MMS spacecraft measured what happens in a magnetic field with intermediate strength: These electrons dance a hybrid, meandering motion — spiraling and bouncing about before being ejected from the region. This takes away some of the magnetic field’s energy.
4. Surpassing computer simulations
Before we had direct measurements from the MMS mission, computer simulations were the best tool scientists had to study plasma's unusual magnetic behavior in space. But MMS' data has revealed that these processes are even more surprising than we thought — showing us new electron-scale physics that computer simulations are still trying to catch up with. Having such detailed data has spurred theoretical physicists to rethink their models and understand the specific mechanisms behind magnetic reconnection in unexpected ways.

5. In deep space & nuclear reactions
Although MMS studies plasma near Earth, what we learn helps us understand plasma everywhere. In space, magnetic reconnection happens in explosions on the Sun, in supernovas, and near black holes.
These magnetic explosions also happen on Earth, but only under the most extreme circumstances: for example, in nuclear fusion experiments. MMS' measurements of plasma's behavior are helping scientists better understand and potentially control magnetic reconnection, which may lead to improved nuclear fusion techniques to generate energy more efficiently.

This quartet of spacecraft was originally designed for a two-year mission, and they still have plenty of fuel left — meaning we have the chance to keep uncovering new facets of plasma's intriguing behavior for years to come. Keep up with the latest on the mission at nasa.gov/mms.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
All aboard for the International Space Station!
Before research can get on a rocket to head to space, it is carefully prepared at Kennedy Space Center.

Scientists sometimes spend days, or even weeks, doing all of the last-minute preparations to get their investigation ready for microgravity.

This week on NASA Explorers, we follow a team of researchers in the final days before their experiment gets loaded into a SpaceX Dragon capsule that will carry their research to the space station.

Watch episode 4 here!
Follow NASA Explorers on Facebook to catch new episodes of season 4 every Wednesday!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Becoming a Space Scientist

Astronauts train all over the world, including at Johnson Space Center. Here, they learn not just how to live aboard the International Space Station, but also how to conduct science in microgravity.

Astronauts serve as the eyes and hands of researchers while their experiments are in space, so they must be trained in everything from using a microscope, to maintaining the equipment for combustion experiments.

Check out this week’s episode of NASA Explorers as we go to class with an astronaut.
Follow NASA Explorers on Facebook to catch new episodes of season 4 every Wednesday!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
You Don’t Have to be a Rocket Scientist to Conduct Research in Microgravity

Putting your life’s work on top of a rocket may seem like a daunting task, but that’s exactly what scientists have been doing for decades as they launch their research to the International Space Station.
This season on #NASAExplorers, we’re exploring why we send science to space, and what it takes to get it there!

Watch this week’s episode to meet a team of researchers who are launching an experiment to space for the first time.
Follow NASA Explorers on Facebook to catch new episodes of season 4 every Wednesday!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Go Behind the Scenes of Science in Space

Gravity rules everything on Earth, from how our bodies develop to what our research can reveal, but what happens when we go 250 miles up to the International Space Station?

Get ready to go behind the scenes of what it takes to get science to space, and meet the people who make it happen.

Introducing Season 4 of NASA Explorers: Microgravity. Floating isn’t just fun. Microgravity could open the door to discovery.
You’ve seen things floating in space, but why does that happen and how does it affect science being conducted aboard the International Space Station?
Microgravity makes the International Space Station the perfect place to perform research that is changing the lives of people on Earth, and preparing us to go deeper into space. This season on our series NASA Explorers, we are following science into low-Earth orbit and seeing what it takes to do research aboard the space station.
Follow NASA Explorers on Facebook to catch new episodes of season 4 every Wednesday!
How is Biotechnology Preparing us to Live on the Moon and Mars?
The adventures awaiting astronauts on future long-duration missions have technologists researching sustainable ways to live away from Earth. We’re using what we know from almost 20 years of a continuous human presence on the International Space Station and looking at new technologies to prepare for missions to the Moon and Mars.

Biotechnology – technology that uses living organisms to make products that provide a new use – is key to this research.
With biotechnology, we’re developing new ways to manufacture medicines, build habitats and more in space. Here are some ways biotechnology is advancing spaceflight and how the same research is reaping benefits on Earth.

Healthy astronauts
Planning ways to supply food for a multi-year mission on the Moon or Mars may require making food and nutrients in space. Our scientists are testing an early version of a potential solution: get microorganisms to produce vital nutrients like those usually found in vegetables. Then, whenever they’re needed, astronauts can drink them down.
The microorganisms are genetically engineered to rapidly produce controlled quantities of essential nutrients. Because the microorganisms and their food source both have a long shelf-life at room temperature and only need water to be activated, the system provides a simple, practical way to produce essential nutrients on-demand. The same kind of system designed for space could also help provide nutrition for people in remote areas of our planet.
Our researchers are evaluating the first batches of BioNutrient samples that came back to Earth after an experimental run on the International Space Station.

Because space travel takes a toll on the human body, we’re also researching how biotechnology can be used to advance the field of regenerative medicine.
Related cells that are joined together are collectively referred to as tissue, and these cells work together as organs to accomplish specific functions in the human body. Blood vessels around the cells vascularize, providing nutrients to the tissue to keep it healthy.
Our Vascular Tissue Challenge offers a $500,000 prize to be divided among the first three teams that successfully create thick, metabolically-functional human vascularized organ tissue in a controlled laboratory environment. The vascularized, thick-tissue models resulting from this challenge will function as organ analogs, or models, that can be used to study deep space environmental effects, such as radiation, and to develop strategies to minimize the damage to healthy cells.
Plant factories
Humans have relied on plants’ medicinal qualities for thousands of years for everything from alleviating minor ailments to curing serious diseases. Now, researchers are trying to simplify the process of turning plants into medicine (i.e. how to make it compact and portable). If successful, the cost of biomanufacturing pharmaceuticals on Earth could go down, and plants could produce medicines in space.

Creating medicine on demand isn’t something we typically do, so we’re turning to experts in the field for help. Researchers at the University of California, Davis are transforming plants into mini-medicine factories for future Mars missions. They’re genetically altering an ordinary type of lettuce so that it produces a protein called parathyroid hormone. This hormone is an approved drug for treating osteoporosis, a common condition where bones become weak and brittle.

This type of research is important to long duration spaceflight. When astronauts land on Mars, they will have spent more than half a year in zero gravity on the flight there, and they’ll need to be strong and ready to explore. Having the technologies needed to treat that possibility, and other unanticipated health effects of long duration spaceflight, is crucial.
Growing habitats
Vitamins aren’t the only thing astronauts could be growing on Mars; we’re exploring technologies that could grow structures out of fungi.
An early-stage research project underway at our Ames Research Center is prototyping technologies that could "grow" habitats on the Moon, Mars and beyond out of life – specifically, fungi and the unseen underground threads that make up the main part of the fungus. These tiny threads build complex structures with extreme precision, networking out into larger structures like mushrooms. With the right conditions, they can be coaxed into making new structures – ranging from a material similar to leather to the building blocks for a planetary home.
The myco-architecture project envisions a future where astronauts can construct a habitat out of the lightweight fungi material. Upon arrival, by unfolding a basic structure made up of dormant fungi and simply adding water, the fungi would grow around that framework into a fully functional human habitat – all while being safely contained to avoid contaminating the external environment.

Recycling waste
Once astronauts arrive on the surface of the Moon or a more distant planet, they’ll have to carefully manage garbage. This waste includes some stuff that gets flushed on Earth.
Today, we’re already using a recycling system on the space station to turn urine into drinking water. Poop on the other hand is contained then disposed of on spacecraft returning to Earth. That won’t be possible on more distant journeys, so, we’re turning to biomanufacturing for a practical solution.
Biology can serve as an effective recycling factory. Microorganisms such as yeast and algae feed on all kinds of things classified as “mission waste.” Processing their preferred form of nourishment generates products that can serve as raw materials used to make essential supplies like nutrients, medicines, plastic and fuel.

By taking a careful look at biological processes, we hope to develop new, lightweight systems to leverage that biology to do some helpful in-space manufacturing.
From Space to Earth
Biotechnology is preparing us for longer space missions to the Moon and then Mars – farther from Earth than humans have ever traveled before. As we prepare for those exciting missions, we’re also conducting research on the space station for the primary benefit of everyone on Earth.
January is National Biotechnology Month. To learn more about some of the ways NASA is using biotechnology to solve challenges in space and improve life on Earth, visit this link.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
That’s a wrap! Thank you for all the great questions.
Keep up with Nick’s journey on and off the station by following him on Twitter at @AstroHague. Follow NASA on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
We’re On a Mission to Study The Zone Where Earth Meets Space!
We’re launching ICON — short for Ionospheric Connection Explorer — a mission to explore the dynamic region where Earth meets space: the ionosphere!

Earth’s ionosphere stretches from 50 to 400 miles above the ground, overlapping the top of our atmosphere and the very beginning of space. The Sun cooks gases there until they lose an electron (or two or three), creating a sea of electrically charged particles. But, the ionosphere also responds to weather patterns from Earth rippling up. These changes are complex and tricky to understand.

That’s why we’re launching ICON! Changes in the ionosphere can affect astronauts, satellites and communications signals we use every day, like radio or GPS. Understanding these changes could help us eventually predict them — and better protect our technology and explorers in space.

ICON will track changes in the ionosphere by surveying airglow. It’s a natural feature of Earth’s that causes our atmosphere to constantly glow. The Sun excites gases in the upper atmosphere, so they emit light. From 360 miles above Earth, ICON will photograph airglow to measure the ionosphere’s winds, composition and temperature. ICON also carries an instrument that will capture and measure the particles directly around the spacecraft.

ICON is scheduled to launch on Oct. 10, on a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket. The night of launch, the rocket is flown up to the sky by Northrop Grumman’s L-1011 Stargazer airplane, which takes off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. From 40,000 feet above the open ocean, the Pegasus XL rocket drops from the plane and free-falls for about five seconds before igniting and carrying ICON into orbit.

NASA TV coverage of the launch starts at 9:15 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10 at nasa.gov/live. You can also follow along on Twitter, Facebook or at nasa.gov/icon.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How does time work in a black hole?
How do blackholes form and how do they move ?
Top 5 Technologies Needed for a Spacecraft to Survive Deep Space
When a spacecraft built for humans ventures into deep space, it requires an array of features to keep it and a crew inside safe. Both distance and duration demand that spacecraft must have systems that can reliably operate far from home, be capable of keeping astronauts alive in case of emergencies and still be light enough that a rocket can launch it.
Missions near the Moon will start when the Orion spacecraft leaves Earth atop the world’s most powerful rocket, the Space Launch System. After launch from Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Orion will travel beyond the Moon to a distance more than 1,000 times farther than where the International Space Station flies in low-Earth orbit, and farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever ventured. To accomplish this feat, Orion has built-in technologies that enable the crew and spacecraft to explore far into the solar system. Let’s check out the top five:

Systems to Live and Breathe
As humans travel farther from Earth for longer missions, the systems that keep them alive must be highly reliable while taking up minimal mass and volume. Orion will be equipped with advanced environmental control and life support systems designed for the demands of a deep space mission. A high-tech system already being tested aboard the space station will remove carbon dioxide (CO2) and humidity from inside Orion. The efficient system replaces many chemical canisters that would consume up to 10 percent of crew livable area. To save additional space, Orion will also have a new compact toilet, smaller than the one on the space station.
Highly reliable systems are critically important when distant crew will not have the benefit of frequent resupply shipments to bring spare parts from Earth. Even small systems have to function reliably to support life in space, from a working toilet to an automated fire suppression system or exercise equipment that helps astronauts stay in shape to counteract the zero-gravity environment. Distance from home also demands that Orion have spacesuits capable of keeping astronaut alive for six days in the event of cabin depressurization to support a long trip home.

Proper Propulsion
The farther into space a vehicle ventures, the more capable its propulsion systems need to be in order to maintain its course on the journey with precision and ensure its crew can get home.
Orion’s highly capable service module serves as the powerhouse for the spacecraft and provides propulsion capabilities that enable it to go around the Moon and back on exploration missions. The service module has 33 engines of various sizes. The main engine will provide major in-space maneuvering capabilities throughout the mission such as inserting Orion into lunar orbit and firing powerfully enough to exit orbit for a return trip to Earth. The other 32 engines are used to steer and control Orion on orbit.
In part due to its propulsion capabilities, including tanks that can hold nearly 2,000 gallons of propellant and a back up for the main engine in the event of a failure, Orion’s service module is equipped to handle the rigors of travel for missions that are both far and long. It has the ability to bring the crew home in a variety of emergency situations.

The Ability to Hold Off the Heat
Going to the Moon is no easy task, and it’s only half the journey. The farther a spacecraft travels in space, the more heat it will generate as it returns to Earth. Getting back safely requires technologies that can help a spacecraft endure speeds 30 times the speed of sound and heat twice as hot as molten lava or half as hot as the sun.
When Orion returns from the Moon it will be traveling nearly 25,000 mph, a speed that could cover the distance from Los Angeles to New York City in six minutes. Its advanced heat shield, made with a material called AVCOAT, is designed to wear away as it heats up. Orion’s heat shield is the largest of its kind ever built and will help the spacecraft withstand temperatures around 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit during reentry though Earth’s atmosphere.
Before reentry, Orion also will endure a 700-degree temperature range from about minus 150 to 550 degrees Fahrenheit. Orion’s highly capable thermal protection system, paired with thermal controls, will protect it during periods of direct sunlight and pitch black darkness while its crews comfortably enjoy a safe and stable interior temperature of about 77 degrees Fahrenheit.

Radiation Protection
As a spacecraft travels on missions beyond the protection of Earth’s magnetic field, it will be exposed to a harsher radiation environment than in low-Earth orbit with greater amounts of radiation from charged particles and solar storms. This kind of radiation can cause disruptions to critical computers, avionics and other equipment. Humans exposed to large amounts of radiation can experience both acute and chronic health problems ranging from near-term radiation sickness to the potential of developing cancer in the long-term.
Orion was designed from the start with built in system-level features to ensure reliability of essential elements of the spacecraft during potential radiation events. For example, Orion is equipped with four identical computers that each are self-checking, plus an entirely different backup computer, to ensure it can still send commands in the event of a disruption. Engineers have tested parts and systems to a high standard to ensure that all critical systems remain operable even under extreme circumstances.
Orion also has a makeshift storm shelter below the main deck of the crew module. In the event of a solar radiation event, we developed plans for crew on board to create a temporary shelter inside using materials on board. A variety of radiation sensors will also be on the spacecraft to help scientists better understand the radiation environment far away from Earth. One investigation, called AstroRad, will fly on Exploration Mission-1 and test an experimental vest that has the potential to help shield vital organs and decrease exposure from solar particle events.

Constant Communication and Navigation
Spacecraft venturing far from home go beyond the Global Positioning System (GPS) in space and above communication satellites in Earth orbit. To talk with mission control in Houston, Orion’s communication and navigation systems will switch from our Tracking and Data Relay Satellites (TDRS) system used by the International Space Station, and communicate through the Deep Space Network.
Orion is equipped with backup communication and navigation systems to help the spacecraft stay in contact with the ground and orient itself if its primary systems fail. The backup navigation system, a relatively new technology called optical navigation, uses a camera to take pictures of the Earth, Moon and stars and autonomously triangulate Orion’s position from the photos. Its backup emergency communications system doesn’t use the primary system or antennae for high-rate data transfer.
Keep up with all the latest news on our newest, state-of-the art spacecraft by following NASA Orion on Facebook and Twitter.
More on our Moon to Mars plans, here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com